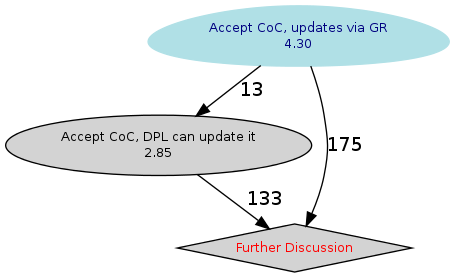
In the graph above, any pink colored nodes imply that the option did not pass majority, the Blue is the winner. The Octagon is used for the options that did not beat the default.
In the following table, tally[row x][col y] represents the votes that option x received over option y. A more detailed explanation of the beat matrix may help in understanding the table. For understanding the Condorcet method, the Wikipedia entry is fairly informative.
| Option | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Option 1 | 128 | 205 | |
| Option 2 | 141 | 228 | |
| Option 3 | 72 | 53 | |
Looking at row 2, column 1, Accept CoC, updates via GR
received 141 votes over Accept CoC, DPL can update it
Looking at row 1, column 2, Accept CoC, DPL can update it
received 128 votes over Accept CoC, updates via GR.
Debian uses the Condorcet method for voting.
Simplistically, plain Condorcets method
can be stated like so :
Consider all possible two-way races between candidates.
The Condorcet winner, if there is one, is the one
candidate who can beat each other candidate in a two-way
race with that candidate.
The problem is that in complex elections, there may well
be a circular relationship in which A beats B, B beats C,
and C beats A. Most of the variations on Condorcet use
various means of resolving the tie. See
Cloneproof Schwartz Sequential Dropping
for details. Debian's variation is spelled out in the
constitution,
specifically, A.6.